As people age, the decline in brain function becomes more apparent. Among individuals aged 20-49, most begin to notice a decline in cognitive function when they experience memory loss or forgetfulness. For those aged 50-59, the realization of cognitive decline often comes when they begin to experience a noticeable drop in memory.
When exploring ways to enhance brain function, different age groups focus on different aspects. People aged 20-29 tend to focus on improving sleep to boost brain performance (44.7%), while individuals aged 30-39 are more interested in reducing fatigue (47.5%). For those aged 40-59, improving attention is considered key to enhancing brain function (40-49 years: 44%, 50-59 years: 43.4%).
Popular Ingredients in Japan's Brain Health Market
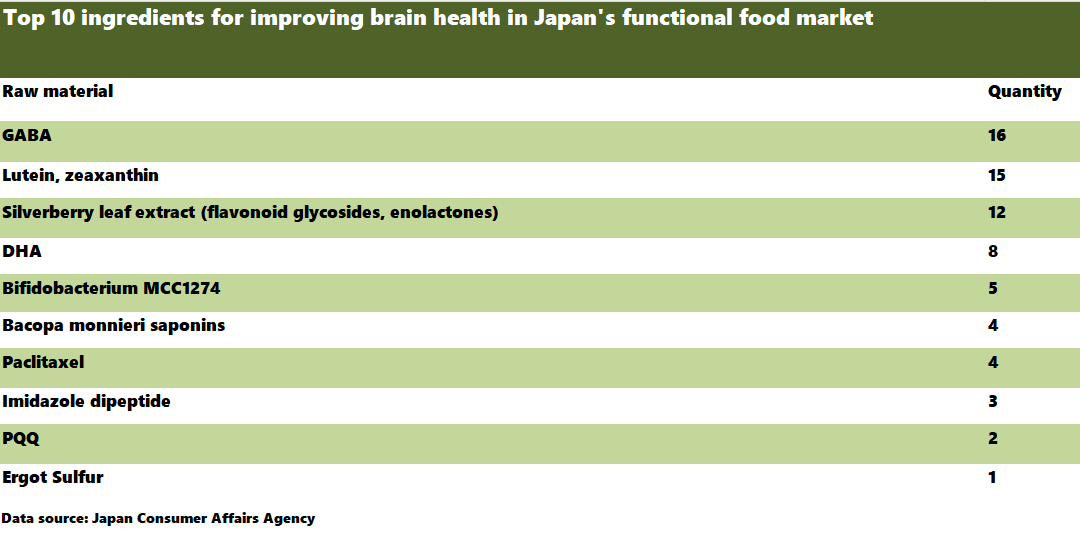
In line with the global trend of pursuing a healthy lifestyle, Japan's functional food market particularly emphasizes solutions for specific health issues, with brain health being a significant focal point. By December 11, 2024, Japan had registered 1,012 functional foods (according to official data), of which 79 were related to brain health. Among these, GABA was the most frequently used ingredient, followed by lutein/zeaxanthin, ginkgo leaf extract (flavonoids, terpenoids), DHA, Bifidobacterium MCC1274, Portulaca oleracea saponins, paclitaxel, imidazolidine peptides, PQQ, and ergothioneine.
1. GABA
GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) is a non-proteinogenic amino acid first detected by Steward and colleagues in potato tuber tissue in 1949. In 1950, Roberts et al. identified GABA in mammalian brains, formed through the irreversible α-decarboxylation of glutamate or its salts, catalyzed by glutamate decarboxylase.
GABA is a critical neurotransmitter found extensively in the mammalian nervous system. Its main function is to reduce neuronal excitability by inhibiting the transmission of neural signals. In the brain, the balance between inhibitory neurotransmission mediated by GABA and excitatory neurotransmission mediated by glutamate is essential for maintaining cell membrane stability and normal neural function.
Studies show that GABA can inhibit neurodegenerative changes and improve memory and cognitive functions. Animal studies suggest that GABA improves long-term memory in mice with cognitive decline and promotes the proliferation of neuroendocrine PC-12 cells. In clinical trials, GABA has been shown to increase serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels and reduce the risk of dementia and Alzheimer's disease in middle-aged women.
In addition, GABA has positive effects on mood, stress, fatigue, and sleep. Research indicates that a mixture of GABA and L-theanine can reduce sleep latency, increase sleep duration, and upregulate the expression of GABA and glutamate GluN1 receptor subunits.
2. Lutein/Zeaxanthin
Lutein is an oxygenated carotenoid composed of eight isoprene residues, an unsaturated polyene containing nine double bonds, which absorbs and emits light at specific wavelengths, giving it unique color properties. Zeaxanthin is an isomer of lutein, differing in the position of the double bond in the ring.
Lutein and zeaxanthin are the primary pigments in the retina. Lutein is mainly found in the peripheral retina, while zeaxanthin is concentrated in the central macula. The protective effects of lutein and zeaxanthin for the eyes include improving vision, preventing age-related macular degeneration (AMD), cataracts, glaucoma, and preventing retinopathy in premature infants.
In 2017, researchers from the University of Georgia found that lutein and zeaxanthin positively influence brain health in older adults. The study indicated that participants with higher levels of lutein and zeaxanthin exhibited lower brain activity when performing word-pair recall tasks, suggesting higher neural efficiency.
Additionally, a study reported that Lutemax 2020, a lutein supplement from Omeo, significantly increased the level of BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor), a critical protein involved in neural plasticity, and crucial for the growth and differentiation of neurons, and associated with enhanced learning, memory, and cognitive function.
(Structural formulas of lutein and zeaxanthin)
3. Ginkgo Leaf Extract (Flavonoids, Terpenoids)
Ginkgo biloba, the sole surviving species in the ginkgo family, is often called a "living fossil." Its leaves and seeds are commonly used in pharmacological research and are one of the most widely used natural medicines worldwide. The active compounds in ginkgo leaf extract are mainly flavonoids and terpenoids, which possess properties such as aiding lipid reduction, antioxidant effects, improving memory, alleviating eye strain, and offering protection against chemical liver damage.
The World Health Organization’s monograph on medicinal plants specifies that standardized ginkgo leaf extracts should contain 22-27% flavonoid glycosides and 5-7% terpenoids, with ginkgolic acid content below 5 mg/kg. In Japan, the Health and Nutrition Food Association has set quality standards for ginkgo leaf extract, requiring flavonoid glycoside content of at least 24% and terpenoid content of at least 6%, with ginkgolic acid kept under 5 ppm. The recommended daily intake for adults is between 60 and 240 mg.
Studies have shown that long-term consumption of standardized ginkgo leaf extract, compared to a placebo, can significantly enhance certain cognitive functions, including memory accuracy and judgment abilities. Moreover, ginkgo extract has been reported to improve brain blood flow and activity.
4. DHA
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) is an omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA). It is abundant in seafood and their products, especially fatty fish, which provide 0.68-1.3 grams of DHA per 100 grams. Animal-based foods such as eggs and meat contain smaller amounts of DHA. Additionally, human breast milk and other mammals' milk also contain DHA. Research on over 2,400 women across 65 studies found that the average concentration of DHA in breast milk is 0.32% of total fatty acid weight, ranging from 0.06% to 1.4%, with coastal populations having the highest DHA concentrations in breast milk.
DHA is associated with brain development, function, and diseases. Extensive research shows that DHA can enhance neurotransmission, neuronal growth, synaptic plasticity, and neurotransmitter release. A meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials showed that an average daily intake of 580 mg of DHA significantly improved episodic memory in healthy adults (18-90 years old) and those with mild cognitive impairment.
DHA’s mechanisms of action include: 1) restoring the n-3/n-6 PUFA ratio; 2) inhibiting age-related neuroinflammation caused by M1 microglial cell overactivation; 3) suppressing the A1 astrocyte phenotype by lowering A1 markers such as C3 and S100B; 4) effectively inhibiting the proBDNF/p75 signaling pathway without altering brain-derived neurotrophic factor-associated kinase B signaling; and 5) promoting neuronal survival by increasing phosphatidylserine levels, which facilitates protein kinase B (Akt) membrane translocation and activation.
5. Bifidobacterium MCC1274
The gut, often referred to as the "second brain," has been shown to have significant interactions with the brain. The gut, as an organ with autonomous movement, can function independently without direct brain instruction. However, the connection between the gut and brain is maintained through the autonomic nervous system, hormonal signals, and cytokines, forming what is known as the "gut-brain axis."
Research has revealed that gut bacteria play a role in the accumulation of β-amyloid protein, a key pathological marker in Alzheimer's disease. Compared to healthy controls, Alzheimer's patients have reduced gut microbiota diversity, with a decrease in Bifidobacterium relative abundance.
In human intervention studies on individuals with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), consumption of Bifidobacterium MCC1274 significantly improved cognitive performance in the Rivermead Behavioral Memory Test (RBANS). Scores in areas such as immediate memory, visual-spatial ability, complex processing, and delayed memory were also significantly improved.
Post time: Jan-07-2025