Astaxanthin (3,3'-dihydroxy-beta,beta-carotene-4,4'-dione) is a carotenoid, classified as a lutein, found in a wide variety of microorganisms and marine animals, and originally isolated from lobsters by Kuhn and Sorensen. It is a fat-soluble pigment that appears orange to deep red in color and does not have vitamin A pro-activity in the human body.
Natural sources of astaxanthin include algae, yeast, salmon, trout, krill and crayfish. Commercial astaxanthin is mainly derived from Fife yeast, red algae and chemical synthesis. One of the best sources of natural astaxanthin is rainfed red chlorella, with an astaxanthin content of about 3.8% (by dry weight), and wild salmon are also good sources of astaxanthin. Synthetic production is still the main source of astaxanthin due to the high cost of large-scale cultivation of Rhodococcus rainieri. The biological activity of synthetically produced astaxanthin is only 50% of that of natural astaxanthin.
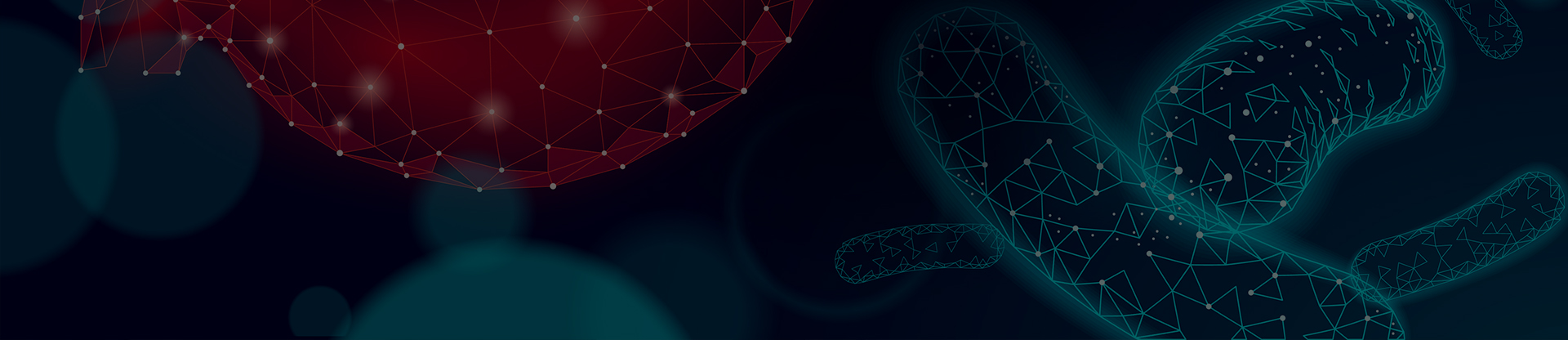
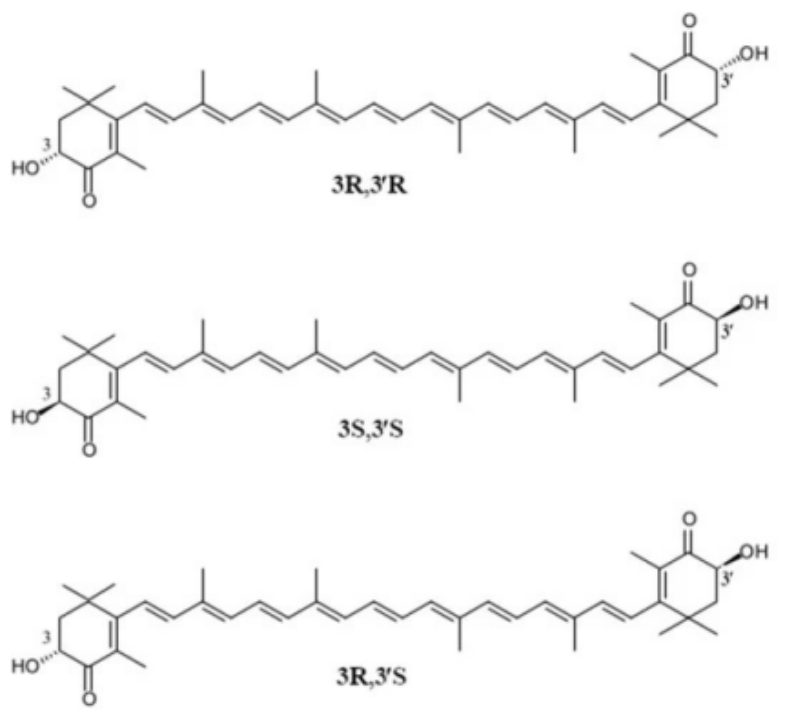
Astaxanthin exists as stereoisomers, geometric isomers, free and esterified forms, with stereoisomers (3S,3'S) and (3R,3'R) being the most abundant in nature. Rhodococcus rainieri produces the (3S,3'S)-isomer and Fife yeast produces the (3R,3'R)-isomer.

Astaxanthin, the heat of the moment
Astaxanthin is the star ingredient in functional foods in Japan.FTA's statistics on functional food declarations in Japan in 2022 found that astaxanthin was ranked No. 7 among the top 10 ingredients in terms of frequency of use, and was mainly used in the health fields of skincare, eye care, fatigue relief, and improvement of cognitive function.
At the 2022 and 2023 Asian Nutritional Ingredients Awards, Justgood Health's natural astaxanthin ingredient was recognized as the best ingredient of the year for two consecutive years, the best ingredient in the cognitive function track in 2022, and the best ingredient in the oral beauty track in 2023. In addition, the ingredient was shortlisted in the Asian Nutritional Ingredients Awards - Healthy Aging track in 2024.
In recent years, academic research on astaxanthin has also begun to heat up. According to PubMed data, as early as 1948, there were studies on astaxanthin, but the attention has been low, starting in 2011, academia began to focus on astaxanthin, with more than 100 publications per year, and more than 200 in 2017, more than 300 in 2020, and more than 400 in 2021.
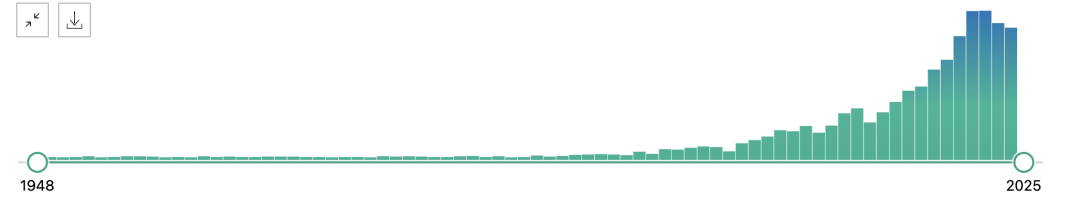
Source of the image:PubMed
In terms of market, according to Future market insights, the global astaxanthin market size is estimated to be USD 273.2 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 665.0 million by 2034, at a CAGR of 9.3% during the forecast period (2024-2034).

Superior antioxidant capacity
Astaxanthin's unique structure gives it superb antioxidant capacity. Astaxanthin contains conjugated double bonds, hydroxyl and ketone groups, and is both lipophilic and hydrophilic. The conjugated double bond at the center of the compound provides electrons and reacts with free radicals to convert them into more stable products and terminate free radical chain reactions in various organisms. Its biological activity is superior to that of other antioxidants due to its ability to connect to cell membranes from the inside out.
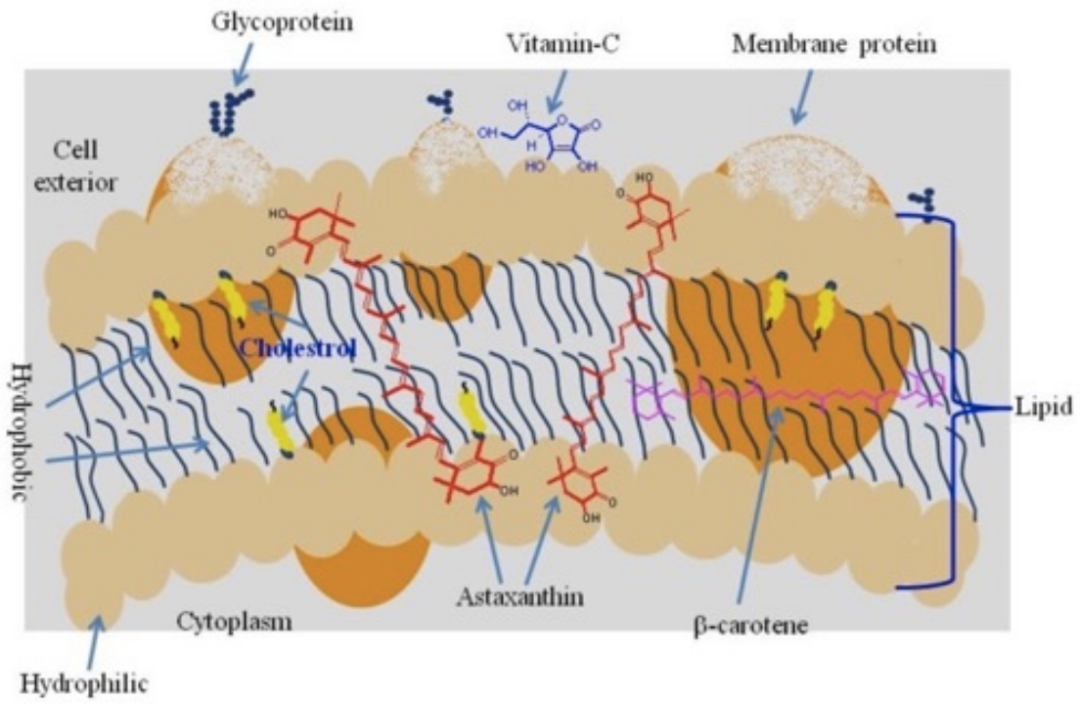
Location of astaxanthin and other antioxidants in cell membranes
Astaxanthin exerts significant antioxidant activity not only through direct scavenging of free radicals, but also through activation of cellular antioxidant defense system by regulating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2) pathway. Astaxanthin inhibits the formation of ROS and regulates the expression of oxidative stress-responsive enzymes, such as heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), which is a marker of oxidative stress.HO-1 is regulated by a variety of stress-sensitive transcription factors, including Nrf2, which binds to antioxidant-responsive elements in the promoter region of detoxification metabolism enzymes.

The full range of astaxanthin benefits and applications
1) Improvement of cognitive function
Numerous studies have confirmed that astaxanthin may delay or improve cognitive deficits associated with normal aging or attenuate the pathophysiology of various neurodegenerative diseases. Astaxanthin can cross the blood-brain barrier, and studies have shown that dietary astaxanthin accumulates in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex of the rat brain after single and repeated intake, which may affect the maintenance and improvement of cognitive function. Astaxanthin promotes nerve cell regeneration and increases gene expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP-2), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and growth-associated protein 43 (GAP-43), proteins that are implicated in brain recovery.
Justgood Health Astaxanthin Capsules, with Cytisine and Astaxanthin from Red Algae Rainforest, synergize to improve cognitive function of the brain.
2) Eye Protection
Astaxanthin has antioxidant activity that neutralizes oxygen free radical molecules and provides protection for the eyes. Astaxanthin works synergistically with other carotenoids that support eye health, especially lutein and zeaxanthin. In addition, astaxanthin increases the rate of blood flow to the eye, allowing the blood to reoxygenate the retina and eye tissue. Studies have shown that astaxanthin, in combination with other carotenoids, protects the eyes from damage across the solar spectrum. In addition, astaxanthin helps relieve eye discomfort and visual fatigue.
Justgood Health Blue Light Protection Softgels, Key ingredients: lutein, zeaxanthin, astaxanthin.
3) Skin Care
Oxidative stress is an important trigger of human skin aging and dermal damage. The mechanism of both intrinsic (chronological) and extrinsic (light) aging is the production of ROS, intrinsically through oxidative metabolism, and extrinsically through exposure to the sun's ultraviolet (UV) rays. Oxidative events in skin aging include DNA damage, inflammatory responses, reduction of antioxidants, and production of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) that degrade collagen and elastin in the dermis.
Astaxanthin can effectively inhibit free radical-induced oxidative damage and the induction of MMP-1 in the skin after UV exposure. Studies have shown that astaxanthin from Erythrocystis rainbowensis can increase collagen content by inhibiting the expression of MMP-1 and MMP-3 in human dermal fibroblasts. In addition, astaxanthin minimized UV-induced DNA damage and increased DNA repair in cells exposed to UV radiation.
Justgood Health is currently conducting several studies, including hairless rats and human trials, all of which have shown that astaxanthin reduces UV damage to the deeper layers of the skin, which cause the appearance of signs of skin aging, such as dryness, sagging skin and wrinkles.
4) Sports nutrition
Astaxanthin can accelerate post-exercise repair. When people exercise or workout, the body produces a large amount of ROS, which, if not removed in time, can damage muscles and affect physical recovery, while astaxanthin's strong antioxidant function can remove ROS in time and repair damaged muscles faster.
Justgood Health introduces its new Astaxanthin Complex, a multi-blend of magnesium glycerophosphate, vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), and astaxanthin that reduces muscle pain and fatigue after exercise. The formula is centered around Justgood Health's Whole Algae Complex, which delivers natural astaxanthin that not only protects muscles from oxidative damage, but also enhances muscle performance and improves athletic performance.

5) Cardiovascular Health
Oxidative stress and inflammation characterize the pathophysiology of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. The superb antioxidant activity of astaxanthin can prevent and improve atherosclerosis.
Justgood Health Triple Strength Natural Astaxanthin Softgels help maintain cardiovascular health by using natural astaxanthin sourced from rainbow red algae, the main ingredients of which include astaxanthin, organic virgin coconut oil and natural tocopherols.
6) Immune Regulation
Immune system cells are very sensitive to free radical damage. Astaxanthin protects the immune system's defenses by preventing free radical damage. A study found that astaxanthin in human cells to produce immunoglobulins, in the human body astaxanthin supplementation for 8 weeks, astaxanthin levels in the blood increased, T cells and B cells increased, DNA damage is reduced, C-reactive protein significantly reduced.
Astaxanthin softgels, raw astaxanthin, use natural sunlight, lava-filtered water and solar energy to produce pure and healthy astaxanthin, which can help enhance immunity, protect vision and joint health.
7) Relieve Fatigue
A 4-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-way crossover study found that astaxanthin promoted recovery from visual display terminal (VDT)-induced mental fatigue, attenuating elevated plasma phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxide (PCOOH) levels during both mental and physical activity. The reason may be the antioxidant activity and anti-inflammatory mechanism of astaxanthin.
8) Liver protection
Astaxanthin has preventive and ameliorative effects on health problems such as liver fibrosis, liver ischemia-reperfusion injury, and NAFLD. Astaxanthin can regulate a variety of signaling pathways, such as reducing JNK and ERK-1 activity to improve hepatic insulin resistance, inhibiting PPAR-γ expression to reduce hepatic fat synthesis, and down-regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 expression to inhibit HSCs activation and liver fibrosis.

Status of regulations in each country
In China, astaxanthin from the source of rainbow red algae can be used as a new food ingredient in general food (except baby food), in addition, the United States, Canada and Japan also allow astaxanthin to be used in food .
Post time: Dec-05-2024



